Planning an EV charging station installation requires absolute precision. The success of your EV charging station dimensions, from legal compliance to user satisfaction, depends on getting the EV charging station dimensions right. The core challenge is that this information is scattered across dozens of different sources.
This guide solves that problem by consolidating everything you need into one place. A compliant and successful installation requires mastering three distinct dimensional areas:
Equipment Dimensions: The physical size of the charger itself.
Space Dimensions: The legally mandated layout of the parking stall, especially for ADA compliance.
Site Element Dimensions: The necessary clearances and protective features like bollards and signage.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through each of these three areas with detailed checklists, tables, and diagrams. It is the definitive resource for architects, installers, and property owners to execute a flawless EV Charging Station Design.

The starting point for any site plan is the physical size of the Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), the technical term for the charging station. The dimensions vary significantly based on the charging level and type.
Level 2 chargers are the most common type, found everywhere from homes to workplaces. They are one of the main options.
Wall-Mount Units: These are compact and ideal for indoor garages or exterior walls. A typical unit is about 12-18 inches wide, 18-24 inches tall, and 6-9 inches deep.
Pedestal-Mount Units: When installed in a parking lot, these units are mounted on a post. The pedestal is typically 4 to 5 feet tall, with the charger mounted on top. The base requires a small concrete pad for stability.
DC Fast Chargers deliver high power and are physically much larger. As the U.S. Department of Energy notes, their deployment is critical for building out highway charging corridors.
All-in-One Cabinets: Many DCFCs are single, large units. These can be substantial, often standing 6-7 feet tall, 3 feet wide, and 2-3 feet deep.
Dispersed Systems: Some systems separate the large power cabinet from the smaller dispenser that the driver uses. The dispenser might only be 5-6 feet tall, while the power cabinet (which can be placed further away) is much larger. This offers more site design flexibility.
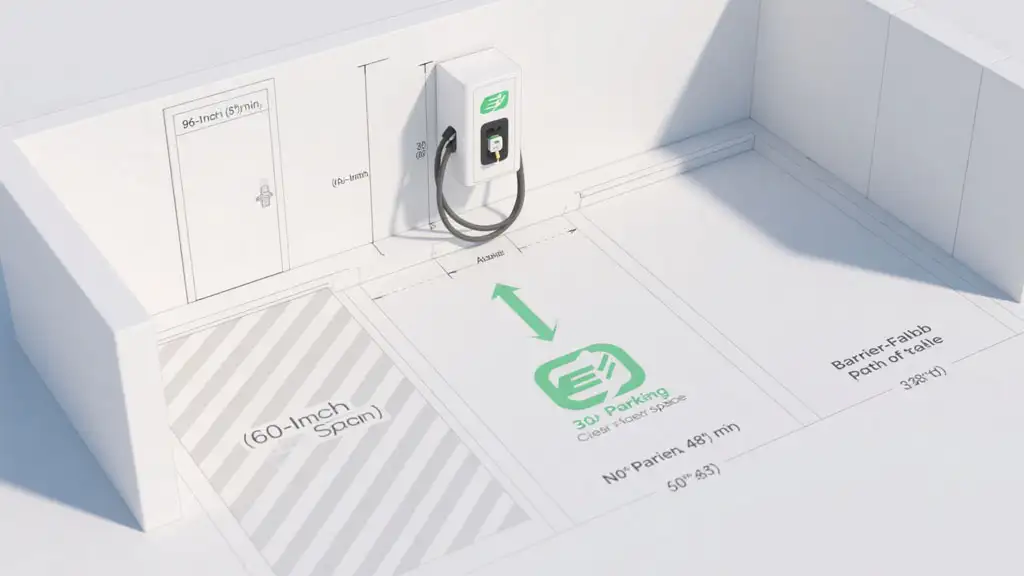
This is the most important and legally mandated set of dimensions. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sets forth clear standards to ensure people with disabilities can access and use EV chargers. Following these is not optional.
Το U.S. Access Board, a federal agency, provides the key technical guidance. According to their rules, accessible spaces are not just about the parking spot itself, but the entire path of travel and clear space around the charger.
Here is a breakdown of the key dimensional requirements from the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design.
Number of Accessible Spaces: The number of required accessible EV charging spaces is determined by the total number of chargers at your site.
Vehicle Space Width: An accessible car space must be at least 96 inches (8 feet) wide. An accessible van space must be at least 132 inches (11 feet) wide.
Access Aisle: Every accessible space must have an adjacent access aisle. This aisle must be at least 60 inches (5 feet) wide for cars and 96 inches (8 feet) wide for vans. The Access Board specifies that this aisle must be marked to prohibit parking in it.
Clear Floor Space: You must provide a clear, level ground space of at least 30 inches by 48 inches for a person in a wheelchair to operate the charger. This space must connect to the access aisle.
Reach Ranges: All operable parts of the charger (screen, buttons, card reader, plug handle) must be within reach. The highest operable part for a forward approach is 48 inches from the ground.
Surface Slope: The parking space, access aisle, and clear floor space cannot have a slope steeper than 1:48 (a 2.08% grade) in any direction.
Properly designed spaces also improve EV Charging Etiquette by giving drivers enough room to maneuver without blocking adjacent spots.
This table, based on the U.S. Access Board’s technical assistance documents, summarizes the key measurements.
ADA Requirement | Dimension Specification (U.S. Standards) | Key Purpose |
Accessible Stall Width (Van) | Minimum 132 inches (11 feet) | Accommodate wider vehicles and lifts. |
Access Aisle Width (Car) | Minimum 60 inches (5 feet) | Allow for wheelchair ramp deployment. |
Clear Floor/Ground Space | Minimum 30 in. x 48 in. | Provide a stable space for operation. |
Max High Forward Reach | 48 inches from ground | Ensure controls are reachable from a seated position. |
Max Slope (All Surfaces) | 1:48 (2.08% grade) | Ensure stability for wheelchairs. |

A professional installation accounts for the supporting elements around the charger. These are critical for safety, durability, and compliance.
Bollards are short, sturdy posts that protect your expensive charging equipment from accidental vehicle collisions. This is a critical consideration for your project’s long-term charging station cost and TCO.
Placement: The U.S. Department of Transportation often recommends bollards be placed at least 36 inches away from the charger to provide a protective buffer.
Spacing: If using multiple bollards, they are typically spaced 4 to 5 feet apart to prevent a vehicle from passing between them.
Pedestal-mounted EVSE units require a concrete pad to ensure they are stable and level. The size of the pad depends on the charger’s weight and local soil conditions, but typical dimensions are 24 x 24 inches for a Level 2 pedestal and 36 x 36 inches or larger for a DCFC.
Signage is critical for identifying charging stations, especially accessible ones. The Federal Highway Administration’s Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) provides standards for sign height and placement to ensure they are visible to drivers.
The charging cable itself has dimensional requirements. It must be long enough to reach the charge port of any vehicle in the space, but it cannot create a hazard.
Effective EV Charger Cable Management systems use retractors or holsters to keep the cable off the ground, preventing tripping hazards and damage to the cable itself.
As we have seen, the topic of EV charging station dimensions is detailed and precise. It is a critical component of the broader EV Charging Standards that govern the industry.
Success is not accidental. It is the result of a deliberate planning process that respects the needs of the user, the requirements of the law, and the physical realities of the site. By mastering the three key dimensions—equipment, space, and site elements—you ensure your project is compliant, user-friendly, and built to last. A well-designed station not only serves its primary function but also promotes good EV Charging Etiquette and reflects positively on your brand.
For complex projects, partnering with an experienced Charge Point Operator or turnkey provider can ensure every detail is handled correctly from start to finish.
U.S. Department of Justice – 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design
National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 625 – via NFPA (National Fire Protection Association)
Federal Highway Administration – Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD)
Θα σας στείλουμε λεπτομερείς τεχνικές πληροφορίες και προσφορά!